Fishing in the Dark: Retrieving Broken Instruments during a Spinal Lumbar Discectomy
Abstract
The equipment utilized in surgical operations must be durable and safe. Regular checks to ensure no signs of wear or fatigue (that may result in failure) should be incorporated into the sterilising and repackaging process. We present a case of equipment failure resulting in a lost foreign body during a lumbar spine discectomy and subsequent difficult retrieval. The potential consequences of such events may be profound for both the patient and the operating team. Lost foreign bodies are typically surgical swabs or needles with resultant complications either acute or delayed. Every effort to prevent such occurrences must be made as patient safety is of the utmost importance.
Introduction
An open lumbar discectomy and hemilaminectomy is a standard surgical option for a patient presenting with lumbar nerve root compression, secondary to a disc herniation and signs of a corresponding neurological deficit [1]. The procedure decompresses the nerve root space and alleviates the harmful compressive effects. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the imaging modality of choice [2] and can clearly display the pathology, location and effects of a disc protrusion which most often occurs at the L5/S1 intervertebral disc level.
Typically, the surgeon will utilise a posterior approach to the spine with the patient in the prone position. A longitudinal incision of approximately 5-7 centimetres over the midline lumbar intervertebral disc. Dissection through the posterior spinous muscles and fascia exposes the disc space on the affected side. The spinal canal space is entered, and a laminectomy performed to decompress the affected nerve root. A discectomy may then be performed if also contributing compressive effects at that level.
The operation is in close proximity to the spinal cord which requires active protection while removing the surrounding lamina and disc. The operative field of view is a narrow-constrained hole several centimetres deep. Bleeding also obscures the view with suction required to assist in maintenance of a dry operative field.
Operative tools must be long and slender with narrow functional operative ranges when used to access the subcentimetre intervertebral spaces. These tools must grasp and cut both bony and soft tissues for removal during a discectomy. Most hospitals reuse most of their spinal tools and equipment, thus instruments remain in circulation for many cycles of sterilization.
Maintenance of this equipment is vital to ensure optimal function, safety and durability. Failure of equipment at critical junctures can lead to unforeseen complications and the potential for profound adverse event. We present a case of an equipment failure and a resultant foreign body lost into the operative field during a lumbar L4/L5 spinal discectomy.
Case Details
A 40-year-old female presented with an acute history of atraumatic right sided lower limb radicular pain, associated with altered motor and sensory function. Clinical assessment demonstrated decreased right ankle dorsiflexion (motor power 3/5) with altered dull sensation over the L4 dermatome. MRI confirmed the pathology to be a L4/L5 posterior disc herniation with unilateral compression of the exiting right nerve L4 root.
An operative open discectomy and hemilaminectomy was performed with the patient in the prone position. No intraoperative spinal monitoring was used.
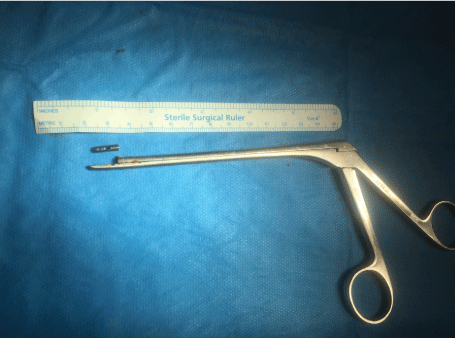
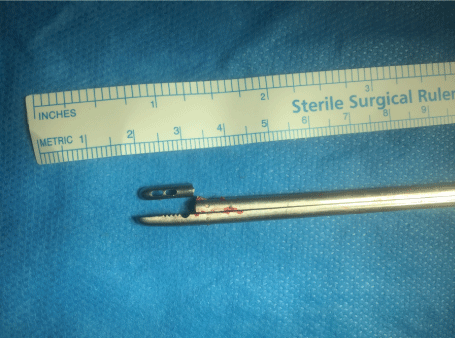
During the operation the intervertebral disc space on the right side was accessed with a hemilaminectomy performed bridging the nerve root. A pituitary rongeur (a metallic grasping forceps, Figure 1 and Figure 2) was used to then excise the herniated disc from the canal and intervertebral space. While the functional tip of the jaws were grasping the disc within the intervertebral space there was an equipment failure. The grasping jaw fractured with the distal fragment disappearing into the remaining disc space, beyond the spinal canal.
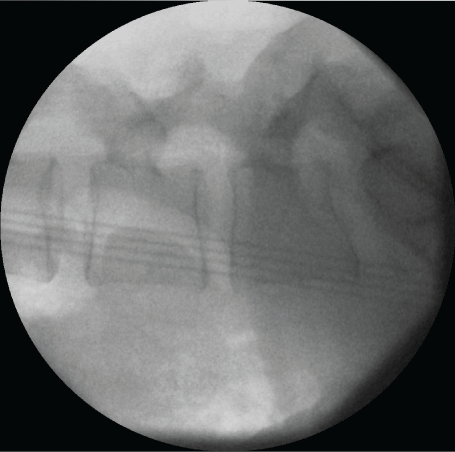
There were repeated unsuccessful attempts to visualize the broken fragment with haemostasis and spinal cord retraction. Multiple attempts of cautious 'blind' extraction into the intervertebral disc space were then carried out and after 15 minutes the fragment was successfully recovered intact. The fragment was aligned with the broken tool to assess for any further deficiency, of which none were determined. Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the fractured pituitary rongeur. Intra-operative radiographs were retained to ensure there were no further radio-opaque fragments (Figure 3).
The wound was closed, and the patient underwent repeated post-operative serial neurological examination. There was no evidence of any new neurological deficits. The preoperative right lower limb neurology resolved over the following weeks and no permanent focal neurology remained after 6 weeks. The patient was informed of the equipment failure and an incident form was submitted as per hospital protocol.
Discussion
This case of an iatrogenic foreign body highlights multiple important issues which are applicable to all surgical disciplines. Any operation with instruments carries the risk of a foreign body that may or may not be retrievable. The most common foreign bodies in surgery are sponges or gauze [3,4], followed by suture needles [5]. A lost or retained foreign body is not one that is routinely discussed in the preoperative consent process with a patient and is definitely not a desirable discussion to be having with a patient after such an occurrence.
Equipment should be routinely checked, maintained and updated. In our case the tools used were not disposable and had been used in circulation for many years. A retrospective review of the set showed they had not been replaced since being acquired several years prior. They had also expired beyond the manufacturers recommended usage date. Hence the cause of the rongeur's failure is almost certainly due to fatigue of the component.
All modern medical equipment purchased now comes with recommended duration of usage, from 'once-off' single use disposable items (e.g. intravenous cannulae, diathermy tips, and sutures), to multi-use, re-usable tools (e.g. drills, forceps, surgical retractors and clamps). Re-usable equipment is cleaned, sterilized and repacked after procedures for repeat usage by the hospital sterile services department. Documentation of purchase date, recommended duration of use and serial inspection for signs of early fatigue or failure is, and should be mandatory to ensure equipment does not fail during use in the operative setting.
The responsibility of ensuring equipment standards lies initially with the producer in delivering safe, high quality equipment. The responsibility lies with the surgeon to ensure their equipment of choice is safe and suitable for use. Should failure arise, and complications ensue the surgeon will often be held responsible. If there is a clinical concern or fault identified, then it is up to the surgeon to refuse usage and ensure safe alternatives or replacements are available. Despite this, there needs to be a degree of clinical governance and responsibility from all staff involved in handling equipment to ensure safety standards and guidelines are adhered to. Theatre equipment stock managers need to be aware of usage, faults and out of date equipment with replacements ordered. Theatre nursing staff and sterilising technicians have a responsibility to inspect equipment for signs of failure and remove such items from circulation. Patient safety is paramount, and our case study demonstrates a series of failures in safety and quality. Incident reports are an important part of the safety process and contribute to internal audit, providing evidence for future policy change to avert a repeat event. The case should also be recorded and presented in the departmental audit meeting, one of the key pillars of clinical governance.
Establishing a system of safety checks and maintenance requires staff, resources and funding. Having evidence of such incidents by audit adds data to support such investment. With the potential for successful medico-legal action [6] in such cases the hospital costs incurred could be substantial and far outweigh the cost of maintaining equipment standards.
Open disclosure, sharing the facts with the patient should be undertaken, as was undertaken with this case. Patient care has evolved into a culture of openness and honesty with full disclosure of such incidents to patients [7]. The incident was discussed with the patient post-operatively, with an apology issued and recognition of the failure to deliver best care. The reaction was positive and appreciated with the relationship and trust maintained between patient and surgeon. This should always be practiced in any similar case, irrespective of the size or location of the foreign body, whether it was retrieved and discussions of the potential complications they may potentially develop. Studies have demonstrated the benefit to both surgeon and patient from such practice [7].
Reports in the literature have shown delayed neurological sequelae from retained foreign bodies in the intervertebral discs. Cases have described evolving neurology [8] and granuloma formation [9] from spinal foreign bodies as well as severe infections in other body locations [10] demonstrating the need and heightened awareness for regular follow up if such cases arise. Patients again should be made aware of potential delayed complications. Examples do exist where the importance of such removal may not be as significant. Ankle syndesmosis screws that fracture on attempted removal remaining buried within a single bone have minimal risk of any sequelae and are often left alone [11]. Despite this, open disclosure must be undertaken with the patient following such events. Consideration should be made to including foreign bodies in the consent process.
Conclusion
Operative equipment failure has the potential to affect all surgical disciplines with the potential for profound consequences to both the patient and surgical team. Surgical instrumentation must undergo the highest scrutiny with early identification and removal before failure arises.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Funding
The authors declare no funding for the study.
References
- Weinstein JN, Lurie JD, Tosteson TD, et al. (2006) Surgical vs. nonoperative treatment for lumbar disk herniation: The Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT) observational cohort. JAMA 296: 2451-2459.
- Bostelmann R, Bostelmann T, Nasaca A, et al. (2017) Biochemical validity of imaging techniques (X-ray, MRI, and dGEMRIC) in degenerative disc disease of the human cervical spine-an in vivo study. Spine J 17: 196-202.
- Serra J, Matias-Guiu X, Calabuig R, et al. (1988) Surgical gauze pseudotumor. Am J Surg 155: 235-237.
- Rappaport W, Haynes K (1990) The retained surgical sponge following intra-abdominal surgery. A continuing problem. Arch Surg 125: 405-407.
- Shafquat Zaman, Robert Clarke, Andrew Schofield (2015) Intraoperative loss of a surgical needle: A laparoscopic dilemma. JSLS 19.
- Rabi Sankar Biswas, Suvro Ganguly, Makhan Lal Saha, et al. (2012) Gossypiboma and surgeon - current medicolegal aspect - A review. Indian J Surg 74: 318-322.
- Elwy AR, Itani KM, Bokhour BG, et al. (2016) Surgeons' Disclosures of Clinical Adverse Events. JAMA Surg 151: 1015-1021.
- Shroyer RN, Fortson CH, Theodotou CB (1960) Delayed neurological sequelae of a retained foreign body (lead bullet) in the intervertebral disc space. J Bone Joint Surg Am 42: 595-599.
- Daniel EF, Smith GW (1960) Foreign-body granuloma of intervertebral disc and spinal canal. J Neurosurg 17: 480-482.
- Susmallian S, Raskin B, Barnea R (2016) Surgical sponge forgotten for nine years in the abdomen: A case report. Int J Surg Case Rep 28: 296-299.
- Naumann MG, Sigurdsen U, Utvag SE, et al. (2016) Incidence and risk factors for removal of an internal fixation following surgery for ankle fracture: A retrospective cohort study of 997 patients. Injury 47: 1783-1788.
Corresponding Author
Matthew Lee, University Hospital Waterford, Dunmore Road, Waterford, Ireland, Tel: 00353-0-86-415-1500.
Copyright
© 2018 Lee M, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.