3D Prostate Reconstruction and Cognitive Fusion to Improve Planning of Retzius Sparing Robotic Assisted Radical Prostatectomy (RS-RARP): Initial Report
Introduction
RARP is a standardized approach to treat localized prostate cancer because offer less morbidity and better functional results [1].
RS-RARP is an emerging technique that promotes faster and better preservation of postoperative continence [2].
Identification of anatomical landmarks in a small space with posterior view of prostate is sometimes harder and some authors said that this technique could be more difficult to achieve proficiency [3].
One of the major criticisms is the difficult localization of lateral end anterior limits of prostate, that can result in positive surgical margins.
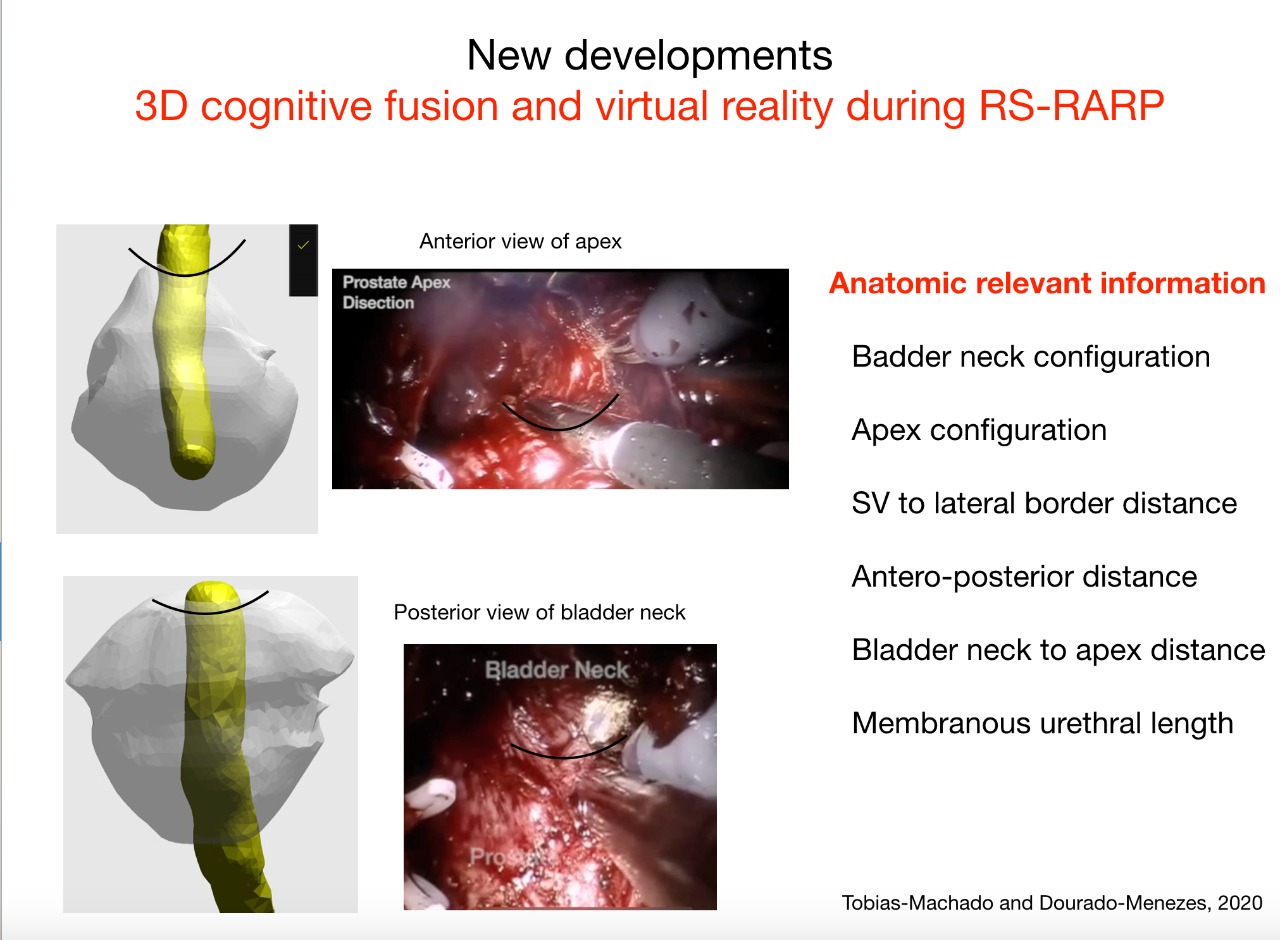
The aim of this report is to present 3D reconstruction as a tool for improve our identification of anatomical details of bladder neck, apex, and lateral borders of prostate during RS-RARP. We expect that better localization of these important anatomical landmarks can improve sexual and urinary function preservation and has potential to reduce surgical margins.
Case Report
50-years-old male with intermediate risk prostate cancer with PSA = 12, clinical stage p T2b and Gleason score = 7(3 + 4). Our propose was RS-RARP. Our figure comparing reconstruction performed at Docdo software and intraoperative endoscopic dissection shows to the perfect correlation between anatomic appearance of bladder neck and prostatic apex. The distance of midline and lateral border evaluate at 3D reconstruction facilitate surgeon to find the exact place between prostatic surface and neurovascular bundle to bilateral preservation. Anterior and posterior dissections were better estimated using length of prostatic urethra and antero posterior diameter. Pathology report shows Bilateral Prostatic Adenocarcinoma Gleason 7(3 + 4), organ confined, free margins. Patients have immediate recovery of continence and full recovery of erection 3 months after surgery (Figure 1).
Discussion
3D reconstruction has been as applied to renal surgery improving CT or MRI evaluation of anatomical details as relation of tumor and vascular or excretory structures that are important to plain complex partial nephrectomies [4].
As the ideal localization of tumor in prostatic image methods of MRI or CT is not ideal, 3D reconstruction is not utilized during RARP.
RS-RARP is a relatively new approach with smaller surgical field and more difficult evaluation of prostatic limits and more positive margins can occur [3].
In this context 3D reconstruction with cognitive fusion of image help surgeon to find better the limits of prostate, aiming to remove all prostatic tissue, preserving functional structures when indicated and possibly reducing positive surgical margins. Other studies with more patients could verify if this new image method will be valuable to facilitate RS-RARP.
References
- Montorsi F, Wilson TG, Rosen RC, et al. (2012) Best practices in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: Recommendations of the Pasadena Consensus Panel. Eur Urol 62: 368-381.
- Genes WP, Bicudo MC, Machado PM, et al. (2019) Retzius sparing (RS) robotic assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) and retzius space reconstruction technique after RARP improve urinary continence compared to conventional RARP (C-RARP): Systematic review and metanalysis. Int Arch Urol Complic 5: 065.
- Dalela D, Jeong W, Prasad MA, et al. (2017) A Pragmatic randomized controlled trial examining the impact of the retzius-sparing approach on early urinary continence recovery after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol 72: 677-685.
- Cacciamani GE, Okhunov Z, Meneses AD, et al. (2019) Impact of three-dimensional printing in urology: State of the art and future perspectives. a systematic review by ESUT-YAUWP group. Eur Urol 76: 209-221.
Corresponding Author
Dr. Marcos Tobias-Machado, Department of Urology, Hospitai São Luis Morumbi Rede D'or, São Paulo, Brazil.
Copyright
© 2021 Tobias-Machado M. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.